ISO (The International Organization for Standardization)
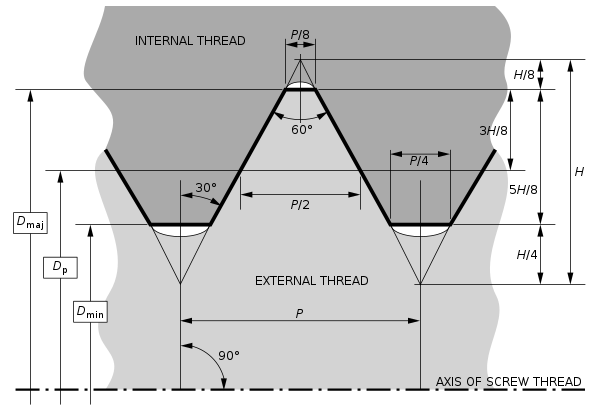
The design principles of ISO general-purpose metric screw threads ("M" series threads) are defined in international standard ISO 68-1.[2] Each thread is characterized by its major diameter, D (Dmaj in the diagram), and its pitch, P. ISO metric threads consist of a symmetric V-shaped thread. In the plane of the thread axis, the flanks of the V have an angle of 60° to each other. The thread depth is 0.54125 × pitch. The outermost 1⁄8 and the innermost 1⁄4 of the height H of the V-shape are cut off from the profile.
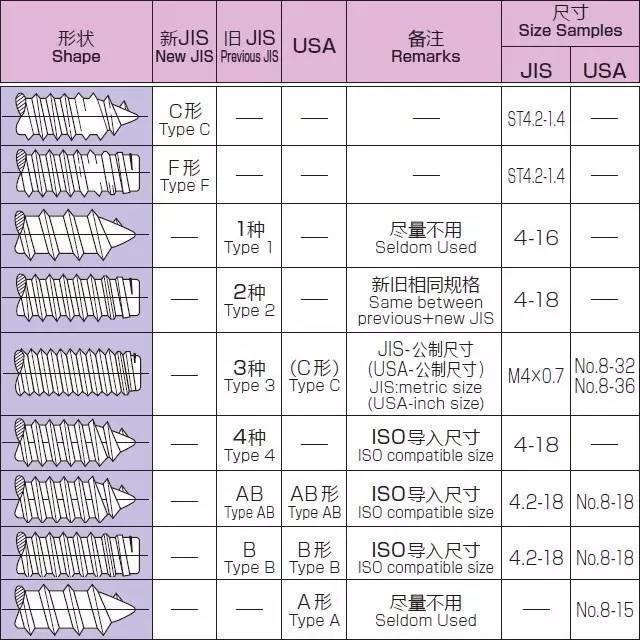
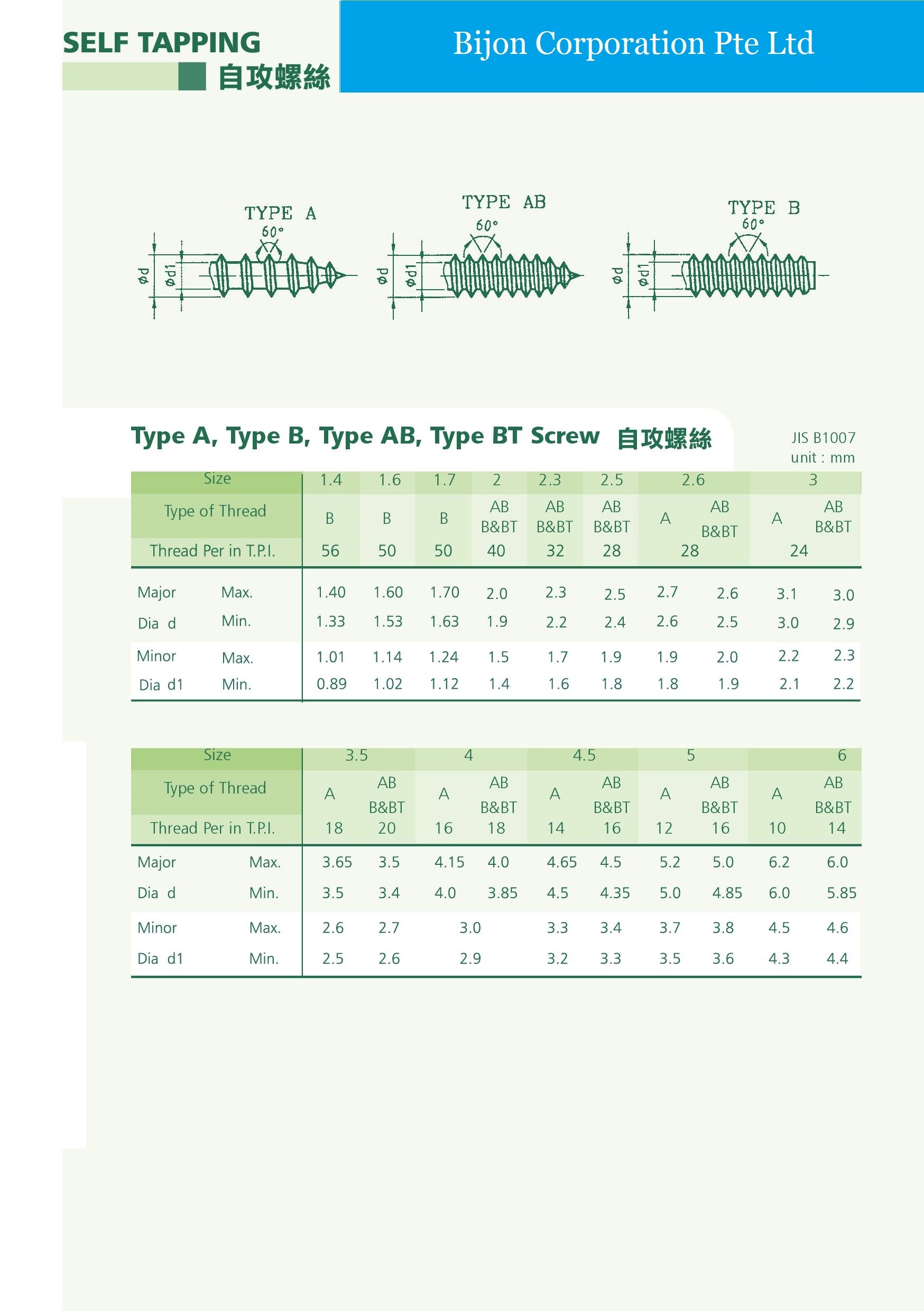
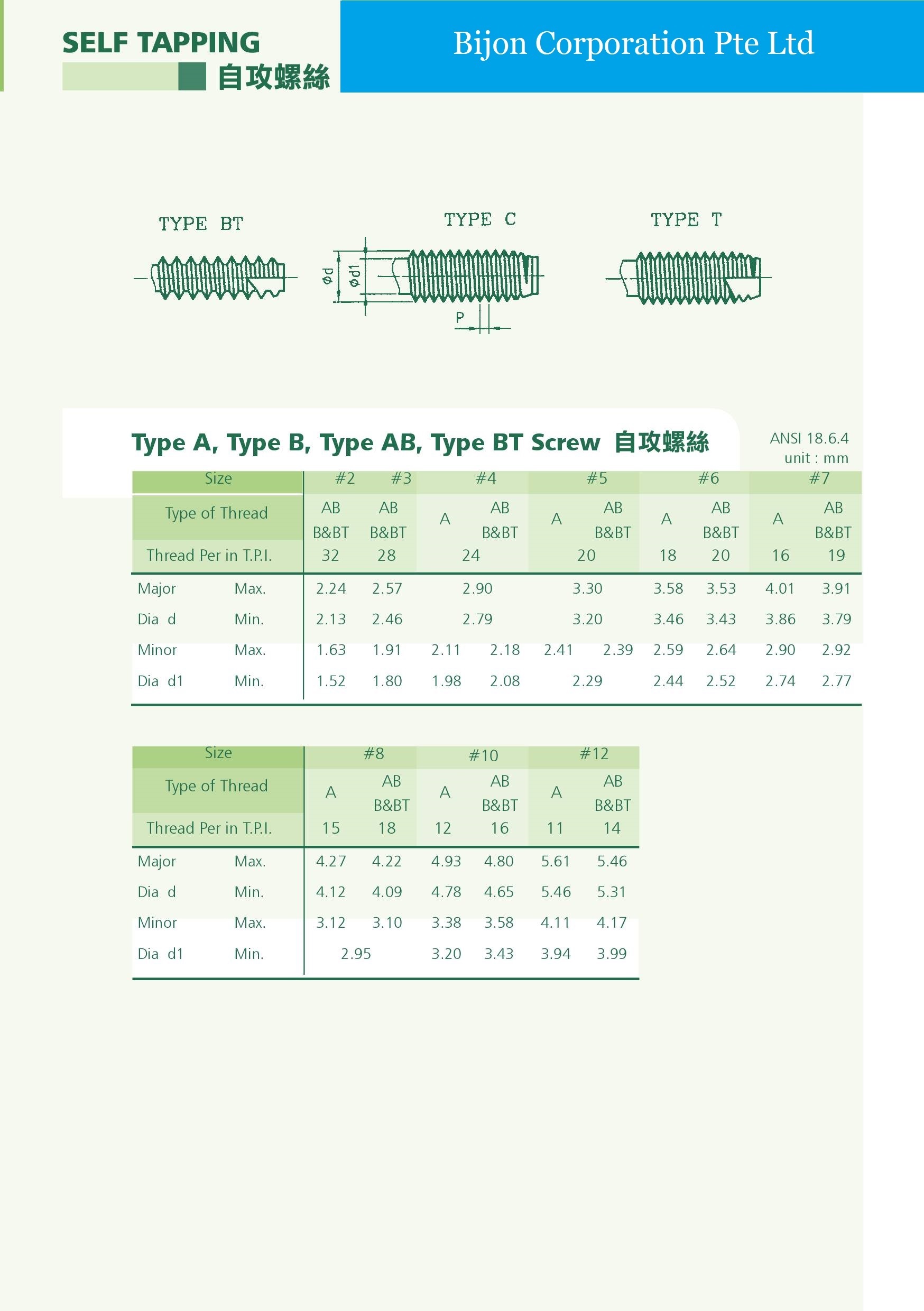
1 ISO metric fastener threads come in coarse, fine, and extra fine series, just as the U.S. inch system threads always have. The usage of coarse to fine threads of ISO threads is about the same as in the inch threads. The overall usage is in the vicinity of 90 percent coarse, 9 percent fine, and 1 percent extra fine. OMFS had no impact on usage in the long run.Thread Chart